面试必问的HashCode技术内幕
tips:面试常问/常用/常出错
hashCode到底是什么?是不是对象的内存地址?
目标:通过一个Demo验证这个hasCode到底是不是内存地址
public native int hashCode();
com.hashcode.HashCodeTest
package com.hashcode; import org.openjdk.jol.vm.VM; import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List; public class HashCodeTest {
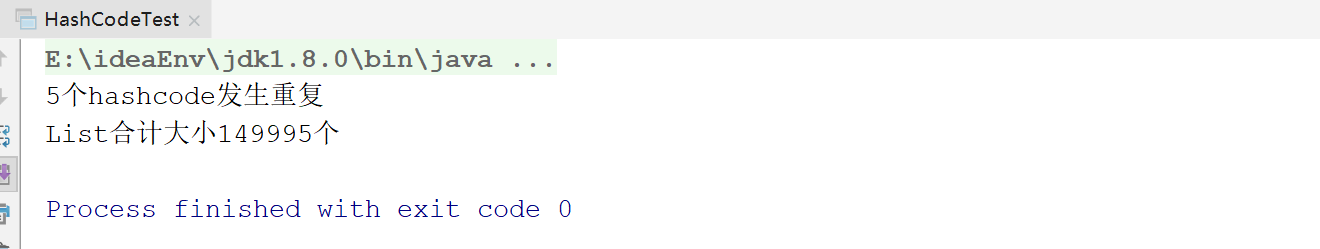
//目标:只要发生重复,说明hashcode不是内存地址,但还需要证明(JVM代码证明)
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 150000; i ) {
//创建新的对象
Object object = new Object();
if (integerList.contains(object.hashCode())) {
num ;//发生重复(内存地址肯定不会重复)
} else {
integerList.add(object.hashCode());//没有重复
}
}
System.out.println(num "个hashcode发生重复");
System.out.println("List合计大小" integerList.size() "个");
}}
15万个循环,发生了重复,说明hashCode不是内存地址(严格的说,肯定不是直接取的内存地址)
思考一下,为什么不能直接用内存地址呢?
提示:jvm垃圾收集算法,对象迁移……
那么它到底是什么?如何生成的呢
既然不是内存地址,那一定在某个地方存着,那在哪里存着呢?
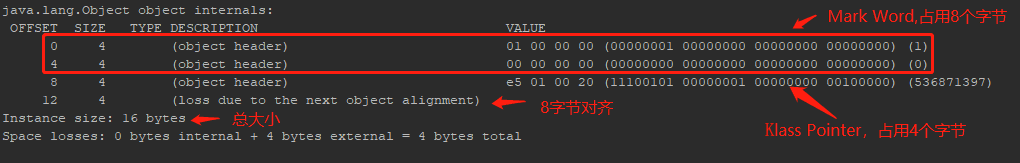
答案:在对象头里!(画图。类在jvm内存中的布局)
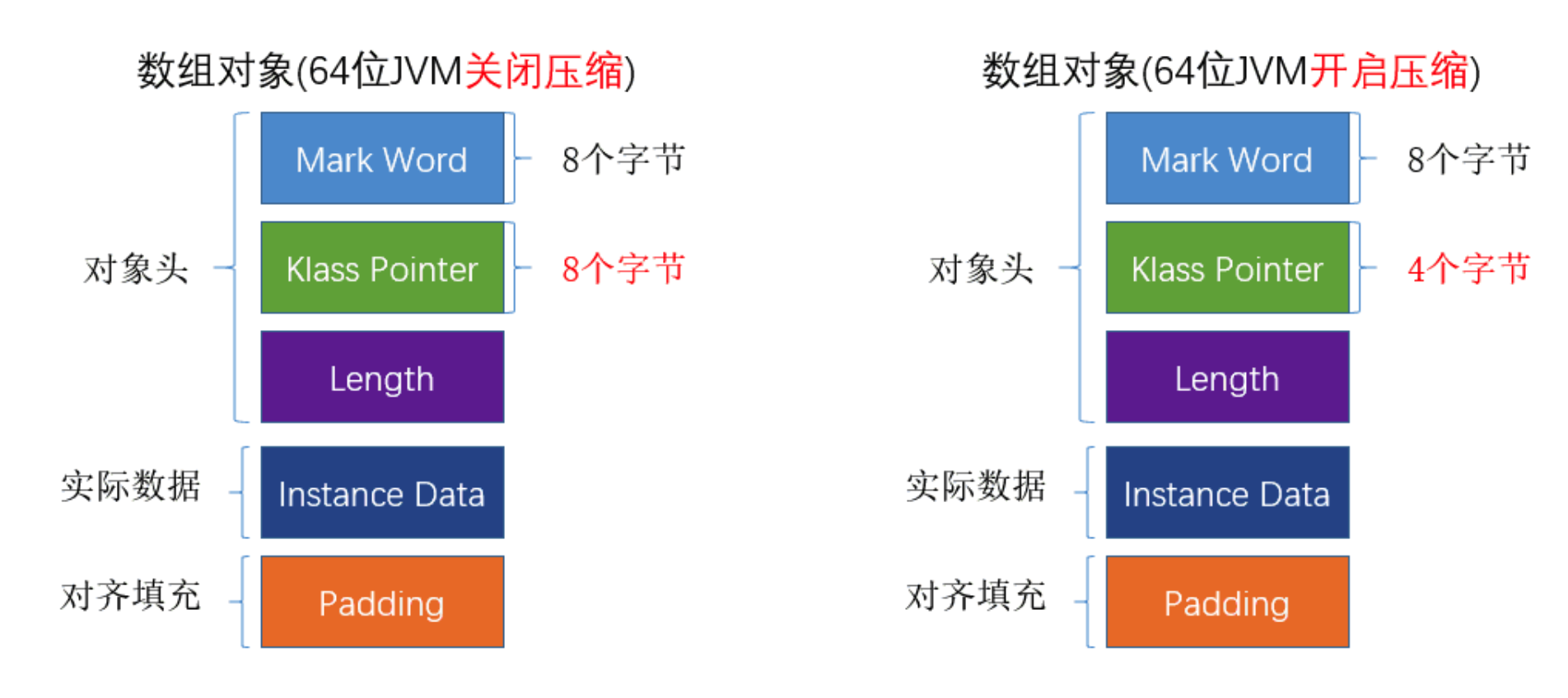
对象头分为两部分,一部分是上面指向class描述的地址Klass,另一部分就是Markword
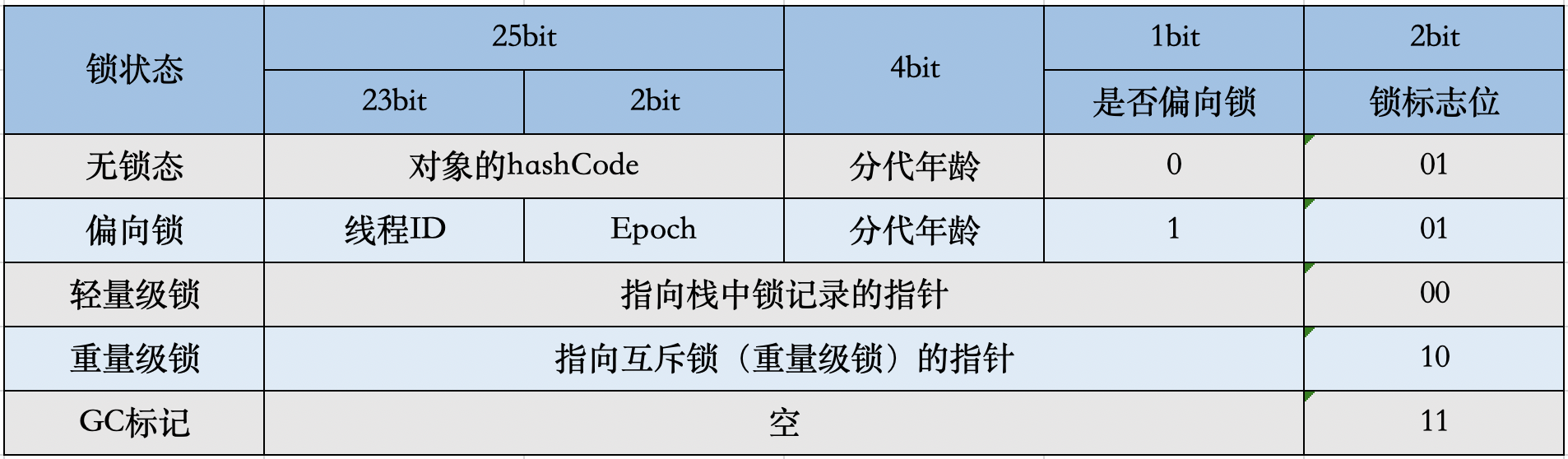
而我们这里要找的hashcode在Markword里!(标记位意义,不用记!)
32位:
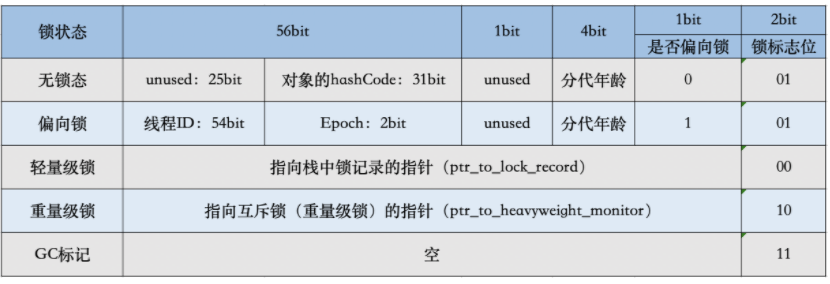
64位:
new的瞬间就有hashcode了吗??
show me the code!我们用代码验证
package com.hashcode; import org.openjdk.jol.info.ClassLayout;import org.openjdk.jol.vm.VM; public class ShowHashCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShowHashCode a = new ShowHashCode();
//jvm的信息
System.out.println(VM.current().details());
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//调用之前打印a对象的头信息
//以表格的形式打印对象布局
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(a).toPrintable());
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//调用后再打印a对象的hashcode值
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a.hashCode()));
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(a).toPrintable());
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//有线程加重量级锁的时候,再来看对象头
new Thread(()->{
try {
synchronized (a){
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(a.hashCode()));
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(a).toPrintable());
} }
结果分析
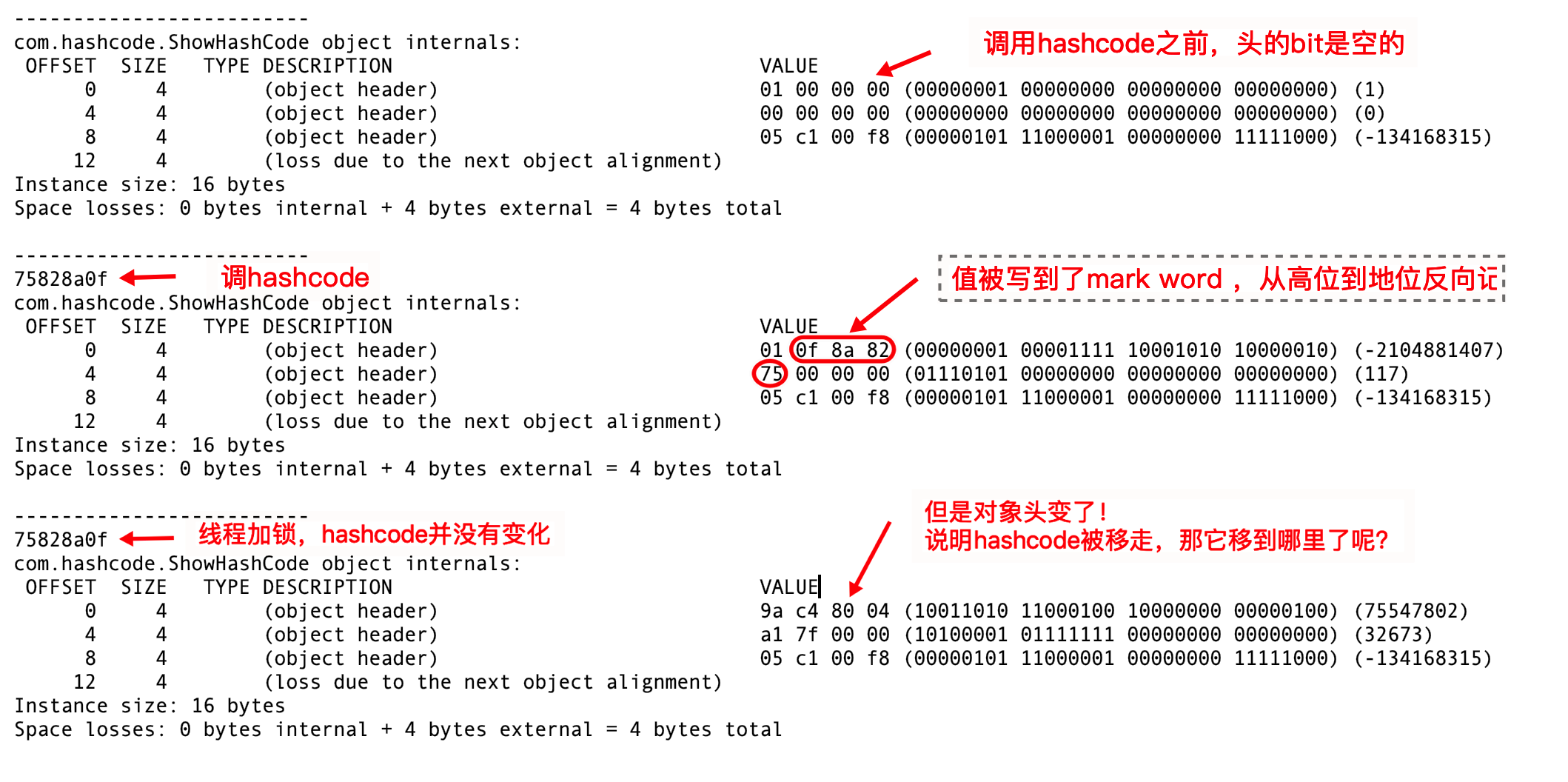
结论:在你没有调用的时候,这个值是空的,当第一次调用hashCode方法时,会生成,加锁以后,不知道去哪里了……
接上文 , 我们追究一下,它详细的生成及移动过程。
我们都知道,这货是个本地方法
public native int hashCode();
那就需要借助上面提到的办法,通过JVM虚拟机源码,查看hashcode的生成
1)先从Object.c开始找hashCode映射
src\share\native\java\lang\Object.c
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL//jni调用//全路径:java_lang_Object_registerNatives是java对应的包下方法Java_java_lang_Object_registerNatives(JNIEnv *env, jclass cls){
//jni环境调用;下面的参数methods对应的java方法
(*env)->RegisterNatives(env, cls,
methods, sizeof(methods)/sizeof(methods[0]));}
JAVA--------------------->C 函数对应
//JAVA方法(返回值)----->C 函数对象static JNINativeMethod methods[] = {
//JAVA方法
返回值 (参数)
c 函数
{"hashCode",
"()I",
(void *)&JVM_IHashCode},
{"wait",
"(J)V",
(void *)&JVM_MonitorWait},
{"notify",
"()V",
(void *)&JVM_MonitorNotify},
{"notifyAll", "()V",
(void *)&JVM_MonitorNotifyAll},
{"clone",
"()Ljava/lang/Object;", (void *)&JVM_Clone},};
JVM_IHashCod在哪里呢?
2)全局检索JVM_IHashCode
完全搜不到这个方法名,只有这个还凑合有点像,那这是个啥呢?
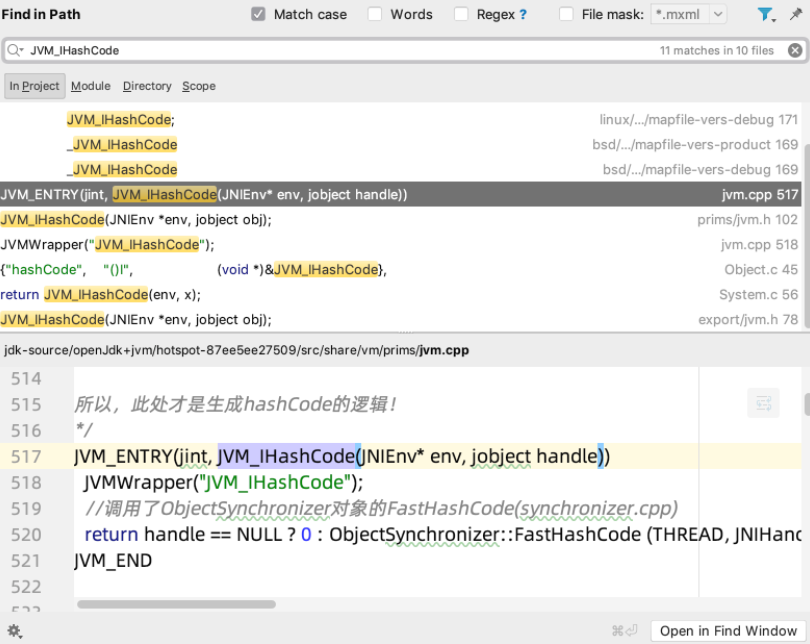
src\share\vm\prims\jvm.cpp
/*JVM_ENTRY is a preprocessor macro thatadds some boilerplate code that is common for all functions of HotSpot JVM API.This API is a connection layer between the native code of JDK class library and the JVM. JVM_ENTRY是一个预加载宏,增加一些样板代码到jvm的所有function中这个api是位于本地方法与jdk之间的一个连接层。 所以,此处才是生成hashCode的逻辑!*/JVM_ENTRY(jint, JVM_IHashCode(JNIEnv* env, jobject handle)) JVMWrapper("JVM_IHashCode"); //调用了ObjectSynchronizer对象的FastHashCode return handle == NULL ? 0 : ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (THREAD, JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(handle)) ;JVM_END
3)继续,ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode
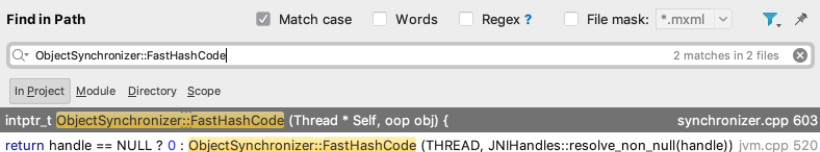

先说生成流程,留个印象:

intptr_t ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (Thread * Self, oop obj) {
//是否开启了偏向锁(Biased:偏向,倾向) if (UseBiasedLocking) {
//如果当前对象处于偏向锁状态
if (obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern()) {
Handle hobj (Self, obj) ;
assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||
!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(),
"biases should not be seen by VM thread here");
//那么就撤销偏向锁(达到无锁状态,revoke:废除)
BiasedLocking::revoke_and_rebias(hobj, false, JavaThread::current());
obj = hobj() ;
//断言下,看看是否撤销成功(撤销后为无锁状态)
assert(!obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern(), "biases should be revoked by now");
} } // …… ObjectMonitor* monitor = NULL; markOop temp, test; intptr_t hash; //读出一个稳定的mark;防止对象obj处于膨胀状态; //如果正在膨胀,就等他膨胀完毕再读出来 markOop mark = ReadStableMark (obj);
//是否撤销了偏向锁(也就是无锁状态)(neutral:中立,不偏不斜的) if (mark->is_neutral()) {
//从mark头上取hash值
hash = mark->hash();
//如果有,直接返回这个hashcode(xor)
if (hash) {
// if it has hash, just return it
return hash;
}
//如果没有就新生成一个(get_next_hash)
hash = get_next_hash(Self, obj); // allocate a new hash code
//生成后,原子性设置,将hash放在对象头里去,这样下次就可以直接取了
temp = mark->copy_set_hash(hash); // merge the hash code into header
// use (machine word version) atomic operation to install the hash
test = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(temp, obj->mark_addr(), mark);
if (test == mark) {
return hash;
}
// If atomic operation failed, we must inflate the header
// into heavy weight monitor. We could add more code here
// for fast path, but it does not worth the complexity.
//如果已经升级成了重量级锁,那么找到它的monitor
//也就是我们所说的内置锁(objectMonitor),这是c里的数据类型
//因为锁升级后,mark里的bit位已经不再存储hashcode,而是指向monitor的地址
//而升级的markword呢?被移到了c的monitor里 } else if (mark->has_monitor()) {
//沿着monitor找header,也就是对象头
monitor = mark->monitor();
temp = monitor->header();
assert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
//找到header后取hash返回
hash = temp->hash();
if (hash) {
return hash;
}
// Skip to the following code to reduce code size } else if (Self->is_lock_owned((address)mark->locker())) {
//轻量级锁的话,也是从java对象头移到了c里,叫helper
temp = mark->displaced_mark_helper(); // this is a lightweight monitor owned
assert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
hash = temp->hash();
// by current thread, check if the displaced
//找到,返回
if (hash) {
// header contains hash code
return hash;
} }
......略
问:
为什么要先撤销偏向锁到无锁状态,再来生成hashcode呢?这跟锁有什么关系?
答:
mark word里,hashcode存储的字节位置被偏向锁给占了!偏向锁存储了锁持有者的线程id
(参考上面的markword图)
扩展:关于hashCode的生成算法(了解)
// hashCode() generation :// 涉及到c 算法领域,感兴趣的同学自行研究// Possibilities:// * MD5Digest of {obj,stwRandom}// * CRC32 of {obj,stwRandom} or any linear-feedback shift register function.// * A DES- or AES-style SBox[] mechanism// * One of the Phi-based schemes, such as:// 2654435761 = 2^32 * Phi (golden ratio)// HashCodeValue = ((uintptr_t(obj) >> 3) * 2654435761) ^ GVars.stwRandom ;// * A variation of Marsaglia's shift-xor RNG scheme.// * (obj ^ stwRandom) is appealing, but can result// in undesirable regularity in the hashCode values of adjacent objects// (objects allocated back-to-back, in particular). This could potentially// result in hashtable collisions and reduced hashtable efficiency.// There are simple ways to "diffuse" the middle address bits over the// generated hashCode values://static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread * Self, oop obj) { intptr_t value = 0 ; if (hashCode == 0) {
// This form uses an unguarded global Park-Miller RNG,
// so it's possible for two threads to race and generate the same RNG.
// On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the
// mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic.
value = os::random() ;//返回随机数 } else if (hashCode == 1) {
// This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent)
// between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0
// synchronization schemes.
//和地址相关,但不是地址;右移 异或算法
intptr_t addrBits = cast_from_oop<intptr_t>(obj) >> 3 ;
value = addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom ;//随机数位移异或计算 } else if (hashCode == 2) {
value = 1 ;
// 返回1 } else if (hashCode == 3) {
value = GVars.hcSequence ;//返回一个Sequence序列号 } else if (hashCode == 4) {
value = cast_from_oop<intptr_t>(obj) ;//也不是地址 } else {
//常用
// Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state
// This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll
// likely make this the default in future releases.
//马萨利亚教授写的xor-shift 随机数算法(异或随机算法)
unsigned t = Self->_hashStateX ;
t ^= (t << 11) ;
Self->_hashStateX = Self->_hashStateY ;
Self->_hashStateY = Self->_hashStateZ ;
Self->_hashStateZ = Self->_hashStateW ;
unsigned v = Self->_hashStateW ;
v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8)) ;
Self->_hashStateW = v ;
value = v ; }
通过分析虚拟机源码我们证明了hashCode不是直接用的内存地址,而是采取一定的算法来生成
hashcode值的存储在mark word里,与锁共用一段bit位,这就造成了跟锁状态相关性
如果是偏向锁:
一旦调用hashcode,偏向锁将被撤销,hashcode被保存占位mark word,对象被打回无锁状态
那偏偏这会就是有线程硬性使用对象的锁呢?
对象再也回不到偏向锁状态而是升级为重量级锁。hash code跟随mark word被移动到c的object monitor,从那里取
- 0003
- 0000
- 0001
- 0000
- 0005